Screening
What is vision screening?
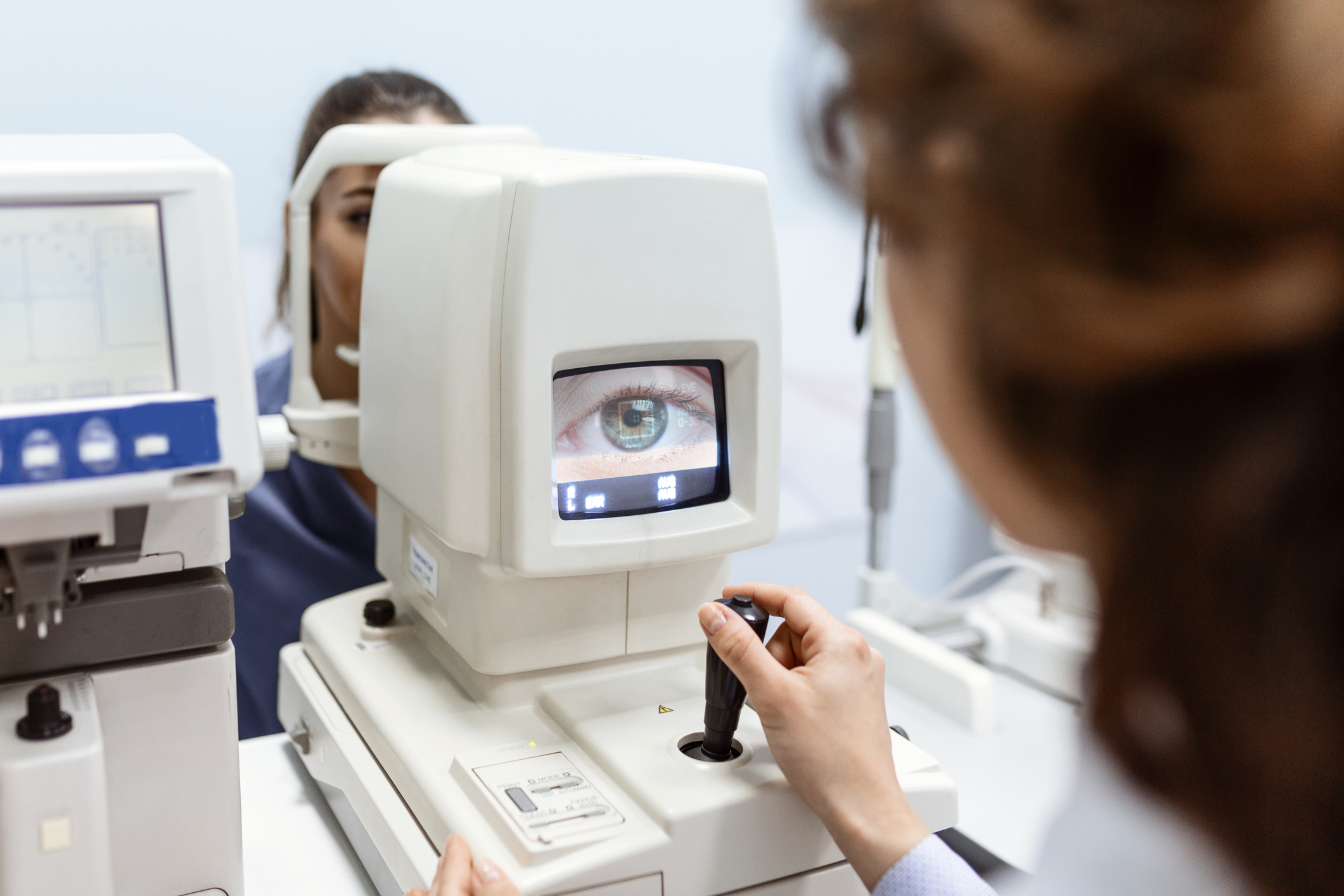
Screening involves a health professional carrying out various examinations, with varying degrees of detail depending on the context, to detect any visual pathologies or vision problems. During medical monitoring, it is important to detect risk factors and to spot the warning signs of any eye pathologies, so that they can be treated as soon as possible.
The ophthalmologist
This screening is carried out by a health professional qualified in the field of visual pathologies: the ophthalmologist, also known as an ophthalmologist.
An ophthalmologist is a medical doctor who specialises in the diagnosis and treatment of eye problems, as well as diagnosing systemic diseases that manifest themselves as eye signs or symptoms. He is also responsible for performing surgery and issuing prescriptions for glasses and contact lenses.
The ophthalmologist can be consulted directly, without a prescription from the general practitioner.
Ophthalmologists may work simultaneously or separately, in a practice, clinic or hospital.
In summary, an ophthalmologist provides :
- Preventive eye and vision care;
- Diagnosis of eye problems and diseases;
- Medical and surgical treatment of all eye problems and related issues.
According to the Canadian Ophthalmological Society, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist in the following cases:
- Loss or absence of vision in one or both eyes
- Changes in vision such as sudden flashes, lightning, irregular streaks or streams of light, wavy or watery vision, blurred faces, distortions or wavy lines, halos, double vision
- Changes in the field of vision such as shadows, hazy vision, black spots or blurred vision in the centre or periphery (side) of the field of vision
- Physical changes to the eye such as crossed eyes, eyes turning inwards, outwards, upwards or downwards, pain, signs of infection (redness, swelling, discharge, etc.)
- Changes in colour vision
The various screening tests
Various eye examinations are carried out, depending on the context:
- Corneal topography
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- High-frequency ocular ultrasound (UBM)
- Measurement of the central curvature of the cornea (Keratometry)
- Measurement of central corneal thickness (corneal pachymetry)
- Specular microscopy of corneal endothelial cells
- Simple retinophotographs and retinophotographs with colour filters
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- Retinal angiography
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- HRT
- GDX
- Papilla photographs
- Conventional and high-frequency ultrasound (UBM)
- Biometry using IOLmaster
Orthoptic assessment
- Examination of colour vision
- Visual field
- Automatic refraction
- Aberrometry
- Electrophysiology: visual evoked potentials (VEP); electroretinogram (ERG); electro-oculogram (EOG)
Orthoptists
The orthoptist is a health professional and medical auxiliary who provides rehabilitation and re-education of the visual function, and takes part in screening for visual disorders, in collaboration with the ophthalmologist. Orthoptists are authorised to carry out eye examinations, measure visual acuity and define corrective optical power on medical prescription.
The majority of orthoptists consult in private practices, but some also work in hospitals and clinics.
The orthoptic assessment enables an orthoptic diagnosis to be made and a treatment plan to be drawn up. It is carried out on the basis of the patient's pathology and age, the complaints described and the patient's own needs in relation to his or her activities. It is a visual capacity assessment.
The optometrist
Optometry is an independent health profession. The main skills of an optometrist are carrying out refractive examinations, eye function tests, external and internal eye inspections and fitting contact lenses.
Secondly, the optometrist proposes appropriate optical solutions such as spectacle lenses, contact lenses or specific low vision equipment.
Depending on the case, recommendations will also be made for muscle re-education with an orthoptist or follow-up with an ophthalmologist.
Source: Swiss Optometry
