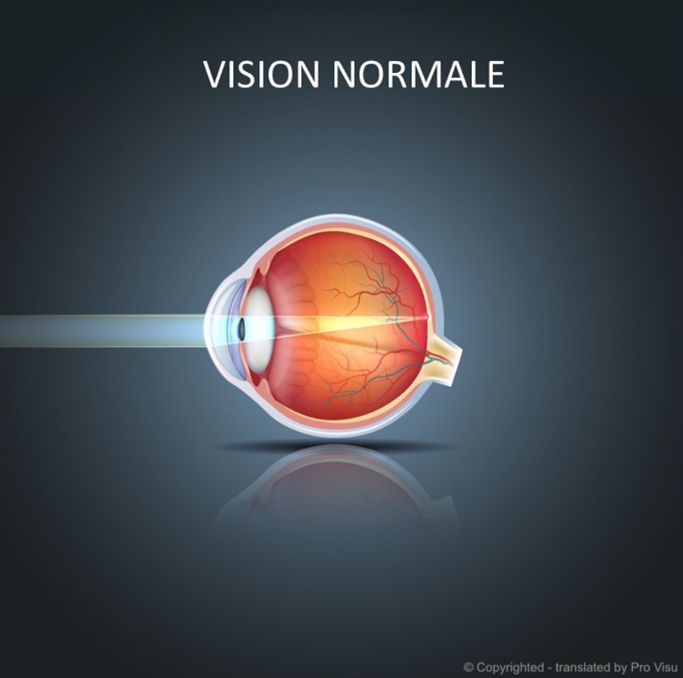
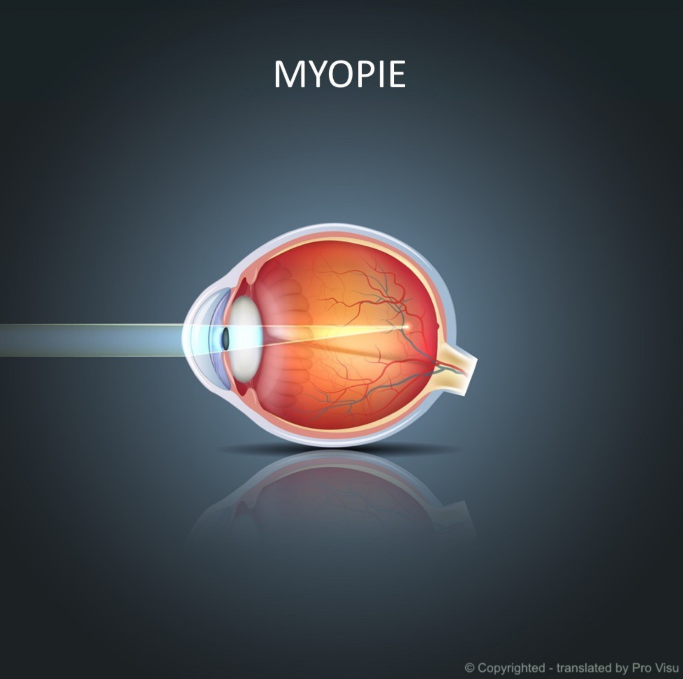
Diseases
Myopia

Definition
Myopia is a very common refractive error (in fact, it is said to be an epidemic among children), characterized by blurred distance vision. Instead of converging on the retina, the light rays that form the image perceived by the eye are projected ahead of it. As a result, the image appears more smeared and blurred.
Causes
There is a clear hereditary component to this refractive disorder: having a myopic parent doubles the risk of also being myopic, and eight-fold if both parents are myopic.
Young age is also a contributing factor, as children are more likely to develop excessive eye lengthening as they grow. From the age of twenty onwards, myopia tends to stabilize.
Lifestyle can also contribute to myopia. In fact, the increase in time spent indoors to the detriment of time spent outdoors is problematic for the eyes. When we're indoors, we prefer activities that require close-up vision (screens, tablets, computers, reading) and constant accommodation of the eyes.
Symptoms
People with myopia have blurred vision of things at a distance, but can see clearly up close. This means they have to approach an object or person to see it clearly. Certain situations may be suggestive:
difficulty in easily recognizing an individual across the street
The tendency to sit close to the screen or stage at the cinema or theater so as to be able to see the actors' faces.
The difficulty children and teenagers have in reading what is written on a blackboard or projected onto a screen. In fact, myopia is often detected at school or study time.
Another sign of myopia is squinting to compensate and see distant objects more clearly.
Diagnosis
If you find it difficult to see at a distance, you should have a visual acuity test followed by a refraction test carried out by an ophthalmologist or optometrist. In children and young adults, it is often necessary to instill drops in the eyes to guarantee reliable measurements.
Treatments
Myopia can be corrected by wearing glasses or contact lenses. Both are adjusted to the degree of correction the myopic person needs. In children, the progression of myopia can sometimes be slowed by the use of highly diluted Atropine eye drops. Certain types of contact lenses or glasses fitted with special lenses can also slow the development of myopia. Laser treatment, performed on an outpatient basis, offers excellent results in adults. Refractive surgery aims to flatten the cornea, after which glasses or contact lenses are no longer required.
Frequency
Myopia is on the increase worldwide, particularly in children. It is estimated that it affects around 40% of the population, including 5 to 10% with high myopia. Within 30 years, it could affect almost half the world's population.
Prevention
Children should spend at least one hour outdoors in natural light every day, to reduce the risk of developing or worsening myopia. It's important to take advantage of every opportunity to play outdoors and to be exposed to natural light, both of which are considered protective for the eyes. In outdoor activities, distance vision (or gaze at a distance) is put to greater use, and the eye doesn't need to make constant efforts to accommodate as it does for near vision. What's more, natural light increases the secretion of dopamine, a hormone that limits eye growth. Artificial light does not have this protective effect. It's worth noting that the risk of developing myopia in children is reduced by a factor of three if they are exposed to outdoor light for two hours a day, even if there is a family history of myopia.
For indoor activities, we recommend keeping a distance of 30 cm between your eyes and a book, smartphone or screen.
Finally, it's important not to overlook the fact that high myopia is not without consequences. If left untreated, it can lead to eye complications such as premature cataract, retinal detachment, glaucoma, strabismus and more.
References
La moitié de la population mondiale sera myope en 2050 - Planete sante
Myopie - Hôpital ophtalmique Jules-Gonin
Swiss Visio - Myopie | Swiss Medical Network
La myopie est en forte augmentation dans le monde - SWI swissinfo.ch